




















Some material in this lecture is adapted from the teaching materials of the book “Web Services: Concepts, Architectures and Applications” and is thus Copyright © 2003 Gustavo Alonso, ETH Zürich and/or Copyright © 2004 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg.
All other material is Copyright © 2006 Kenneth M. Anderson
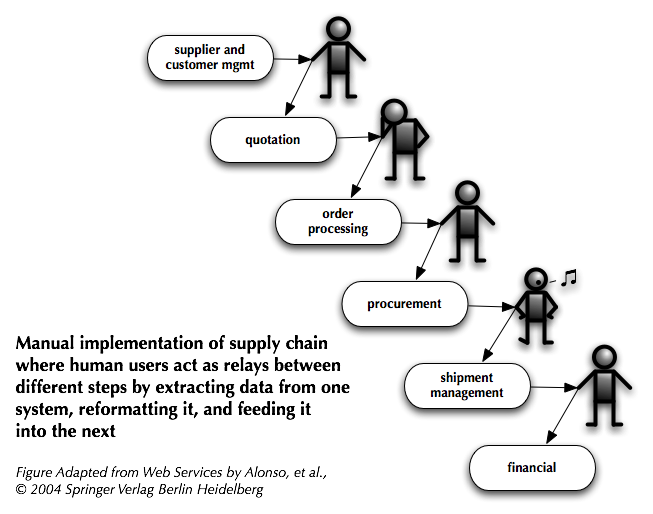
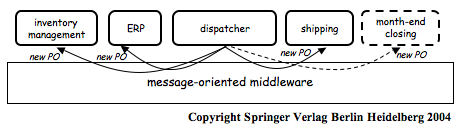
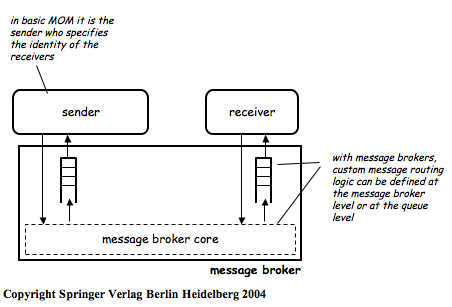
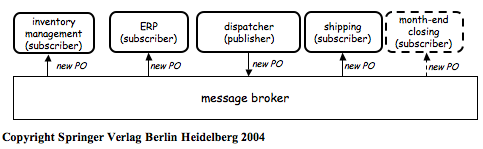
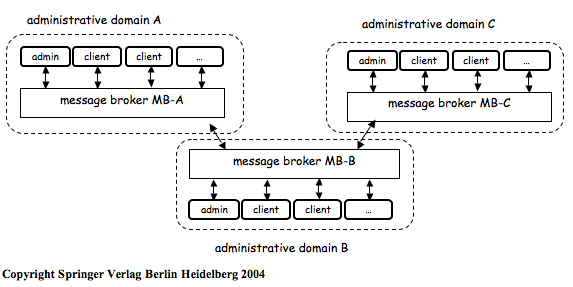
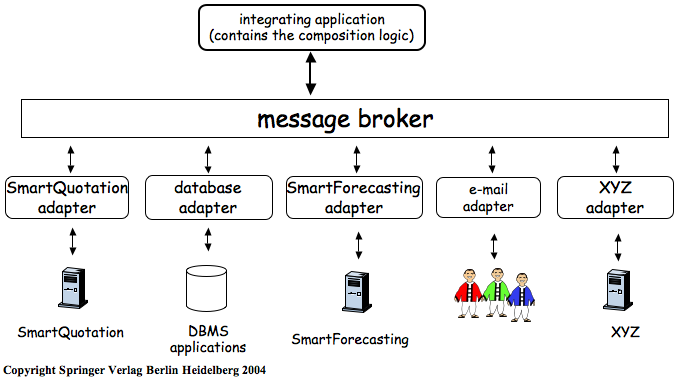
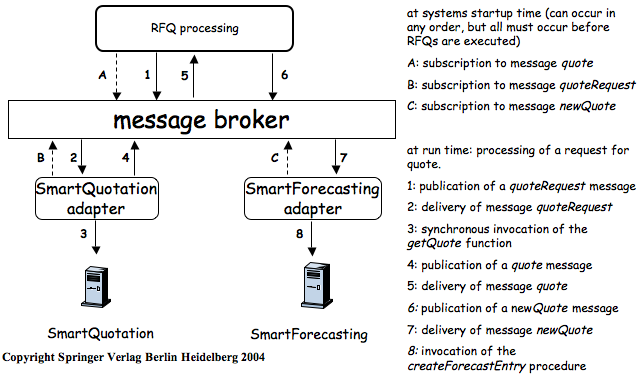
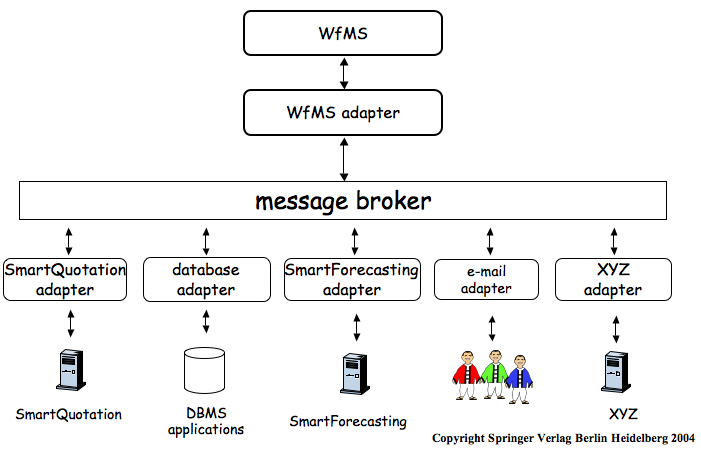
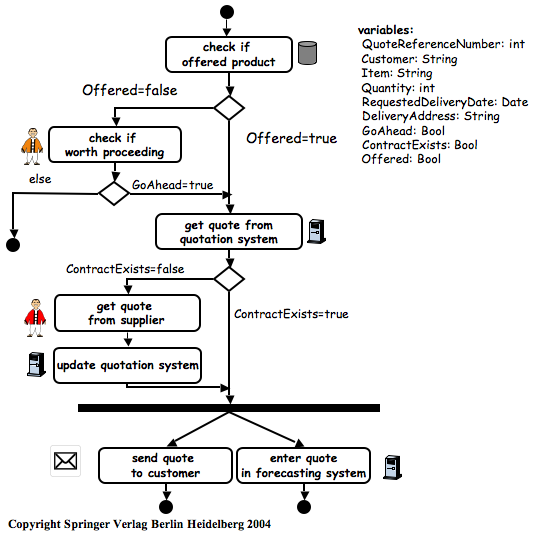
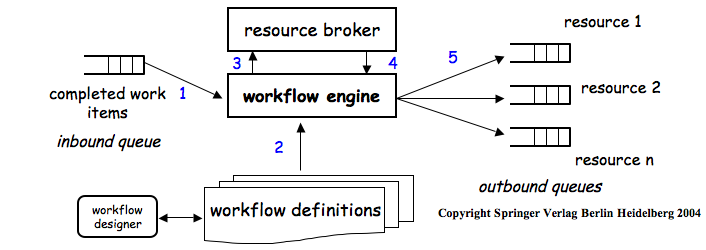
Initially, middleware was used to construct new systems… Later, it was used to distribute [application logic] and to integrate [servers of 3-tier architectures]… When these systems are very different in nature and functionality, using conventional middleware to integrate them becomes rather cumbersome, and in some cases simply infeasible. EAI can be seen as a step forward in the evolution of middleware, extending its capabilities to cope with application integration…
— Introduction to Chapter 3 of our Textbook